GNU / Linux
Documentations > Linux
Posté le 14 novembre 2018 dans Linux par Julien.
Diverses informations à propos de GNU/Linux et de son fonctionnement 🐧
Description
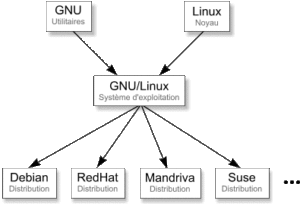
Il existe de nombreux systèmes d’exploitation libres qui sont composés comme tel :
- Noyau : Linux
- Des logiciels : GNU
Il en découle de nombreuses « distributions » qui reposent sur ces composants GNU/Linux, par exemple :
- Debian
- Ubuntu
- RedHat
- KaliLinux
- ArchLinux
- ElementaryOS
- Etc …
Rien de tel qu’un bon schéma pour illustrer le tout 🙂
Organisation des dossiers
bin/ # Programmes (exécutables) susceptibles d'être utilisés par tous les utilisateurs de la machine
boot/ # Fichiers permettant le démarrage de Linux
dev/ # Fichiers contenant les périphériques
etc/ # Fichiers de configuration
- shadow # Contient les hashs des mots de passe
- apache2/ # Dossier de configuration
- - apache2.conf # Fichier de configuration principal d'apache2
- ...
home/ # Répertoires personnels des utilisateurs
- Desktop/ # Le bureau
lib/ # Bibliothèques partagées essentielles et modules du noyau
mnt/ # Point de montage des partitions temporaires
opt/ # Paquetages d'applications logicielles supplémentaires
- plesk/ # Applications Plesk (ex: php)
- ...
root/ # Répertoires personnels de l'utilisateur root
- Desktop/ # Le bureau
sbin/ # Binaires système essentiels
tmp/ # Fichiers temporaires
usr/ # Hiérarchie secondaire
var/ # Données variables
- www/ # Sites web
- - un_site/ # Un site
- - - index.php # index du site
- ...
Raccourcis clavier Terminal
################## Working With Processes ##################
Ctrl+C # Interrupt (kill) the current foreground process running in in the terminal. This sends the SIGINT signal to the process, which is technically just a request—most processes will honor it, but some may ignore it.
Ctrl+Z # Suspend the current foreground process running in bash. This sends the SIGTSTP signal to the process. To return the process to the foreground later, use the fg process_name command.
Ctrl+D # Close the bash shell. This sends an EOF (End-of- file) marker to bash, and bash exits when it receives this marker. This is similar to running the exit command.
################## Tab Completion ##################
Tab # Automatically complete the file, directory, or command you’re typing.
################## Controlling the Screen ##################
Ctrl+L # Clear the screen. This is similar to running the “clear” command.
Ctrl+S # Stop all output to the screen. This is particularly useful when running commands with a lot of long, verbose output, but you don’t want to stop the command itself with Ctrl+C.
Ctrl+Q # Resume output to the screen after stopping it with Ctrl+S.
################## Moving the Cursor ##################
Ctrl+A / Home # Go to the beginning of the line.
Ctrl+E or End # Go to the end of the line.
Alt+B # Go left (back) one word.
Ctrl+B # Go left (back) one character.
Alt+F # Go right (forward) one word.
Ctrl+F # Go right (forward) one character.
Ctrl+XX # Move between the beginning of the line and the current position of the cursor. This allows you to press Ctrl+XX to return to the start of the line, change something, and then press Ctrl+XX to go back to your original cursor position. To use this shortcut, hold the Ctrl key and tap the X key twice.
################## Deleting Text ##################
Ctrl+D / Delete # Delete the character under the cursor.
Alt+D # Delete all characters after the cursor on the current line.
Ctrl+H / Backspace # Delete the character before the cursor.
################## Fixing Typos ##################
Alt+T # Swap the current word with the previous word.
Ctrl+T # Swap the last two characters before the cursor with each other. You can use this to quickly fix typos when you type two characters in the wrong order.
Ctrl+_ # Undo your last key press. You can repeat this to undo multiple times.
################## Cutting and Pasting ##################
Ctrl+W # Cut the word before the cursor, adding it to the clipboard.
Ctrl+K # Cut the part of the line after the cursor, adding it to the clipboard.
Ctrl+U # Cut the part of the line before the cursor, adding it to the clipboard.
Ctrl+Y # Paste the last thing you cut from the clipboard. The y here stands for “yank”.
################## Capitalizing Characters ##################
Alt+U # Capitalize every character from the cursor to the end of the current word, converting the characters to upper case.
Alt+L # Uncapitalize every character from the cursor to the end of the current word, converting the characters to lower case.
Alt+C # Capitalize the character under the cursor. Your cursor will move to the end of the current word.
################## Working With Your Command History ##################
Ctrl+P / Up Arrow # Go to the previous command in the command history. Press the shortcut multiple times to walk back through the history.
Ctrl+N / Down Arrow # Go to the next command in the command history. Press the shortcut multiple times to walk forward through the history.
Alt+R # Revert any changes to a command you’ve pulled from your history if you’ve edited it.
Ctrl+R # Recall the last command matching the characters you provide. Press this shortcut and start typing to search your bash history for a command.
Ctrl+O # Run a command you found with Ctrl+R.
Ctrl+G # Leave history searching mode without running a command.